Family Dynamics, News and Trending Events
Parenting Statistics: Essential Insights for Today’s Families

Parenting is a complex and multifaceted experience that varies across different cultures and societies. Understanding various parenting statistics can provide valuable insights into how parents raise their children, the effectiveness of different parenting styles, and the factors that influence parental decision-making. Examining these statistics can also help identify areas of concern and offer potential solutions to improve the well-being of both children and parents.
Parenting in the United States
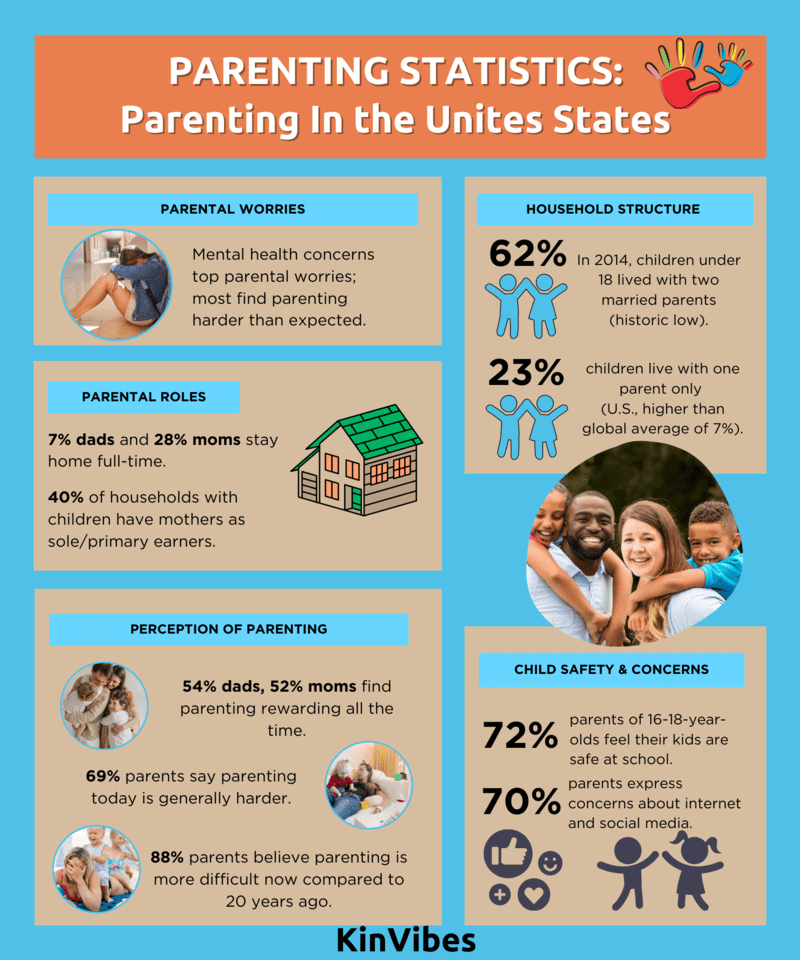
- Mental health concerns top the list of worries for parents; most say being a parent is harder than they expected.
- In 2014, 62% of children younger than 18 lived in a household with two married parents – a historic low.
- Almost a quarter of U.S. children under the age of 18 live with one parent and no other adults (23%), more than three times the share of children around the world who do so (7%).
- 7% of dads and 28% of moms stay at home full-time.
- 54% of dads and 52% of moms report that parenting is rewarding all of the time.
- 40% of all households with children under the age of 18 include mothers who are either the sole or primary source of income for the family.
- For parents of 16-18-year-olds, 72% say their kids are safe at school.
- 69% of parents in the United States declared that parenthood today was generally harder.
- 88% of parents in the United States believe that parenting is more difficult today than it was 20 years ago.
- 70% of parents highlighted internet and social media as primary concerns.

In the United States, there is a diverse range of parenting styles and approaches, influenced by factors such as culture, socio-economic background, and family structure. This results in a broad spectrum of experiences for children and their families. Recent research has focused on the impact of mental health on parenthood, as well as the role that media and the internet play in shaping parenting practices in today’s society.
Fathers vs Mothers
In the United States, the roles of fathers and mothers in parenting have evolved over time. Traditionally, fathers were seen as providers and disciplinarians, while mothers took on nurturing and caregiving responsibilities.
However, recent research shows that fathers are now more involved in their children’s lives and are taking on a greater share of caregiving and domestic tasks source. Despite these improvements, there remains a disparity in the amounts of time and emotional involvement fathers and mothers contribute to their children’s upbringing.
Married Parents vs Single-Parent Household
There are significant differences between married and single-parent households in the United States. The majority (87%) of single-parent families are headed by mothers. These households often face unique challenges such as financial struggles, time constraints, and limited support networks. Married parents typically have greater financial resources and can share caregiving and household responsibilities, making it easier to cater to their children’s needs.
Comparison to 20 Years Ago
Parenting in the United States has changed significantly over the past 20 years. Parents now spend more quality time with their children than in the past. This shift is a result of changes in societal values, family structures, and economic conditions. Emphasis on children’s cognitive development and academic success has led parents to engage in more educational and recreational activities with their children.
Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic
The Covid-19 pandemic has significantly affected parenting in the United States. Mandatory lockdowns forced many parents to work from home and become their children’s primary caregivers and educators. This change put a strain on families, as parents struggled to balance work and childcare responsibilities. The pandemic has also magnified pre-existing disparities in parenting resources and support, highlighting the need for more social services and childcare assistance for families in need.
Parenting Styles and Approaches
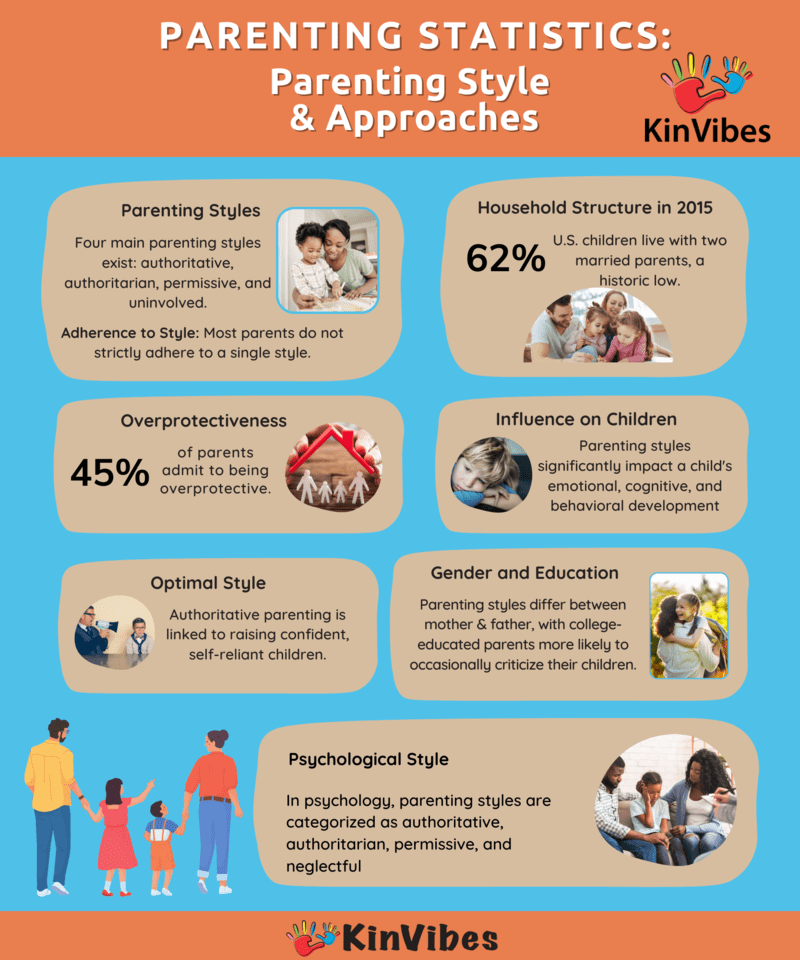
- Four main parenting styles are authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and uninvolved.
- Parenting practices can be looked at in many different ways, but generally, there are four main different types of parenting styles: authoritarian, authoritative, permissive, and neglectful or uninvolved parenting.
- Most parents do not adhere to a specific parenting style.
- 62% of American children under the age of 18 live in a household with two married parents, which is a historic low.
- Parenting styles can influence the way a child feels, thinks, and behaves.
- 45% of parents say they tend to be overprotective.
- Authoritative parenting is the best parenting style for raising self-reliant and confident kids.
- Parenting styles differ between mothers and fathers. (Pew Research Center, 2015)
- College-educated parents are more likely than those who did not attend college to say they sometimes criticize their kids too much.
- The four parenting styles used in psychology are authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and neglectful parenting style.

Discipline and Obedience
Parenting styles can differ significantly in terms of discipline and obedience requirements. One of the most commonly referenced parenting styles is authoritative parenting. This approach encourages parents to set clear expectations and guidelines for their children while also providing the emotional support needed to develop a strong sense of autonomy.
On the other hand, authoritarian parenting focuses more on strict discipline and obedience with little regard for the child’s individuality or emotional needs.
Permissive parenting is another style that contrasts with both authoritative and authoritarian parenting. This approach often involves minimal discipline and allows children to make their own decisions. Permissive parents may struggle to provide adequate guidance and structure, which can potentially lead to a lack of self-control and responsibility in the child.
Freedom and Overscheduling
Modern parenting trends often emphasize the importance of balancing freedom and structure in children’s lives. Authoritative parenting often strikes a balance in this regard, providing a healthy mix of freedom and boundaries.
On the other hand, both authoritarian and permissive parenting styles can lead to imbalances. While authoritarian parents might overly restrict a child’s freedom, permissive parents may inadvertently contribute to an overscheduled life with limited opportunity for unstructured play and individual exploration.
Finding the appropriate balance in regards to freedom and scheduling is essential for a child’s development. This balance can help promote self-confidence, responsibility, and resilience in children as they grow and learn to navigate the world around them.
Role of Praise
Praise can play a crucial role in shaping a child’s motivation and self-esteem. However, the type and frequency of praise should be dependent on the parenting style. Authoritative parents tend to offer praise that is specific, contingent on the child’s effort, and focused on the process rather than the end result. This approach to praise has been shown to foster a growth mindset and promote intrinsic motivation.
By contrast, authoritarian parents might offer less frequent praise or praise that is more focused on outcomes and comparisons to others. This form of praise can potentially promote extrinsic motivation and a fixed mindset. In the case of permissive parenting, praise might be overly abundant, potentially leading to unrealistic expectations and reduced motivation for children to improve through effort and perseverance.
Overall, understanding and implementing various parenting styles, such as authoritative, authoritarian, and permissive parenting, can have a significant impact on a child’s development. Factors such as discipline and obedience, freedom and scheduling, and the role of praise should be carefully considered in order to foster a nurturing environment for children to grow and thrive.
Influence of Social Factors

- Social factors, including peers, family, teachers, and other attachment figures, can influence positive youth development.
- Parental, socioeconomic, and social environmental factors can influence child psychopathology, behavior, and cognitive function.
- Adverse childhood experiences, such as poverty, racial discrimination, stressful home life, and unsafe neighborhoods, can impact children’s behavior and mental health.
- Children brought up in poverty are three times more likely to experience abuse, neglect, or being witness to domestic violence compared with those who were not.
- Socioeconomic status affects family stability, including parenting practices and developmental outcomes for children.
- Individual factors, such as age, gender, and experience playing outdoors, can influence children’s place preferences and play behaviors in outdoor environments.
- Children from low-income families and/or living in deprived neighborhoods tend to play in their immediate surroundings and thus have access to more limited play opportunities.
- Physical factors, such as safety concerns and the design of play spaces, can influence children’s outdoor play.
- Parental concerns about safety, the presence of other children to play with, and bullying behaviors of other children can influence children’s outdoor play.
- Social determinants of health, such as food, social class, employment, work condition, social support, addiction, social governance, and global factors, can affect the growth and development of children.
Effects of Poverty
Poverty can have a significant impact on parenting and child development. Children growing up in low-income households tend to face a range of challenges, including limited access to resources, poor nutrition, and decreased quality of education. Additionally, financial stress can contribute to heightened parental stress, which may, in turn, negatively affect their ability to nurture and discipline their children effectively.
In terms of gender, race, and ethnicity, low-income communities often disproportionately affect marginalized groups, making it crucial to address the specific needs of these populations. Community-based interventions can help increase support and resources for struggling families, thereby improving parenting and the overall well-being of the affected children.
Impact of College Degree
A parent’s educational attainment can also shape their parenting style and their children’s development. Studies have shown that parents with a college degree generally engage in more supportive and stimulating parenting behaviors, leading to better cognitive, emotional, and social outcomes for their children.
Conversely, parents without a college degree might experience difficulty accessing resources or understanding best practices for child-rearing.
It is important to acknowledge the disparities among different racial or ethnic groups regarding educational attainment. Providing equal educational opportunities for all custodial parents can be pivotal in reducing gaps in parenting practices and enhancing children’s well-being across diverse backgrounds.
Single-Parent Household and Teenage Pregnancy
Single-parent households, especially when headed by teenage mothers, often face unique challenges related to parenting.
These could include financial difficulties, emotional distress, and a lack of adequate social support. The limited experience of teenage mothers can result in difficulties navigating the various aspects of child-rearing and balancing the responsibilities of parenting alongside their own development and education.
The impact of these challenges on single-parent households may vary based on race, ethnicity, and community resources. Targeted support, such as mentoring programs or shared parenting networks, can help alleviate the strain on single parents, allowing them to provide the best possible environment for their children’s growth and development.
Mental Health and Parenthood
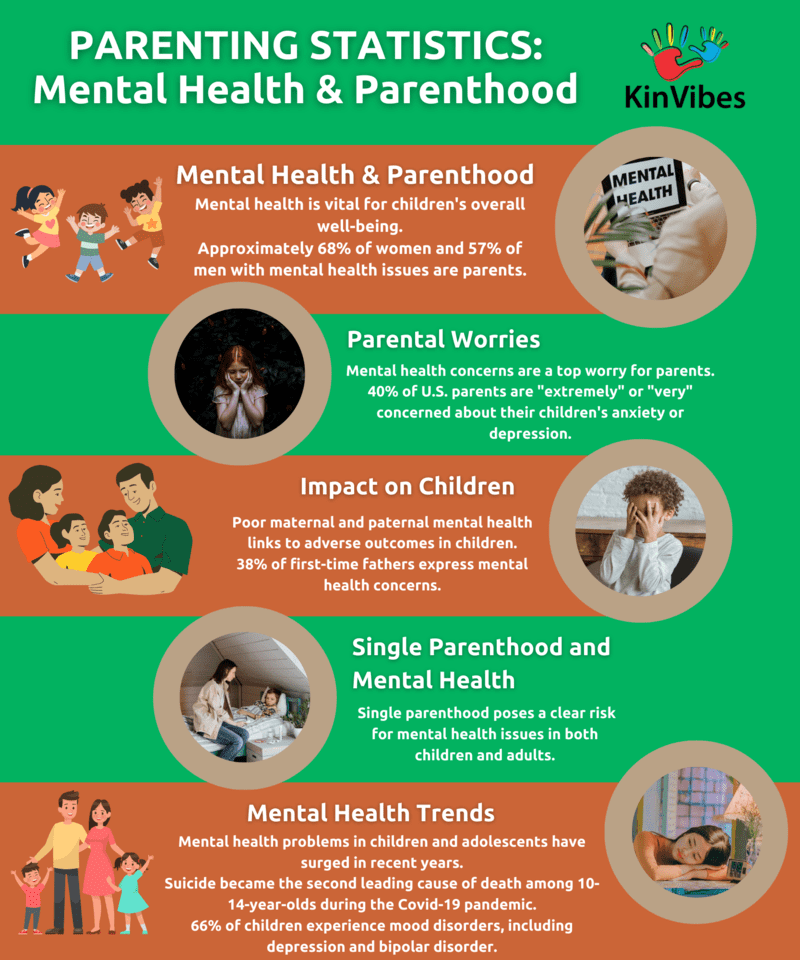
- Mental health is an important part of children’s overall health and well-being.
- Approximately 68% of women and 57% of men with mental health problems are parents.
- Poor maternal and paternal mental health has been associated with poor outcomes in children.
- A 2013/2014 study found that 38% of first-time fathers are concerned about their mental health.
- Mental health concerns top the list of worries for parents.
- 40% percent of US parents are “extremely” or “very” worried that their children will struggle with anxiety or depression at some point.
- Mental health issues among children and adolescents have skyrocketed in recent years.
- Suicide became the second leading cause of death among children 10 to 14 during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- 66% of children had some kind of mood disorder, including depression and bipolar disorder.
- Single parenthood becomes a clear risk factor for mental health problems for both children and adults.
Impact of Overprotective Parenting
Parenting can have a significant impact on the mental health of both parents and children. Overprotective parenting, in particular, has been found to contribute to various mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety.
One study explored the relationship between intensive parenting and maternal mental health, revealing that mothers who felt the pressure to be perfect experienced adverse psychological consequences. Similarly, the time pressure associated with having multiple children has been noted to be a contributing factor to mothers’ worsened mental health.
In the context of children, overprotective parenting can lead to negative outcomes as well. Children of overprotective parents may develop an increased risk for anxiety and depression due to the excessive control and constant monitoring by their parents. Moreover, they may also develop poor coping skills and a low sense of autonomy as they grow older.
Some factors to consider regarding the relationship between overprotective parenting and mental health include:
- The level of parental involvement and control: Excessive control can hinder a child’s development of autonomy and confidence in their abilities, contributing to feelings of anxiety or depression.
- Parents’ mental health: Parents with a history of mental health issues may be more likely to engage in overprotective parenting, potentially leading to further negative consequences for their children.
- The role of societal expectations: Societal pressures can contribute to the development of overprotective parenting styles, as parents may feel the need to adhere to certain ideals to ensure their children’s success.
In conclusion, it is essential to find a balance in parenting that promotes both the mental well-being of parents and the healthy development of children. Overprotective parenting may contribute to negative mental health outcomes for both parties, so awareness and understanding of its potential impact are crucial.
Role of Media and Internet
The impact of media and the internet on parenting and children’s development has become a significant area of concern and study. The digital age has introduced a new set of challenges for parents, including navigating the world of social media, screen time, and internet usage.
Parenting Information and Surveys

A study on New technology role of parents highlights how parents’ beliefs and behavior affect students’ digital media self-efficacy. The data collected in the study reveals that parental guidance and modeling play a crucial role in helping children develop a responsible understanding of technology and its potential effects on their lives.
Social media has become an integral part of contemporary society, and the impact of social media on children and adolescents is an important consideration for parents. Current data suggests that online harassment is less common than offline harassment, and participation in social networking sites does not put most children at risk.
When it comes to screen time, researchers and experts have been working to discover the optimal amount for children. Excessive screen time can contribute to problems in attention, social skills, and overall physical well-being. Guidelines from the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend that children between the ages of 2 and 5 should be limited to no more than one hour of high-quality programming per day, while children aged 6 and older should have consistent limits placed on the amount of daily screen time.
Regarding internet usage, it is essential for parents to take an active role in monitoring and managing their children’s online activities. Teaching them about internet safety should be a priority, as well as establishing rules for appropriate online behavior and communication. Encouraging children to use the Internet for educational and creative purposes can aid in fostering a healthy, balanced relationship with technology.
Concerning Parenting Statistics

Effects of Poverty on Child Development
Poverty is a significant factor that impacts child development. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, in 2019, approximately 10.5% of the U.S. population lived in poverty. Children living in impoverished conditions are more likely to experience health issues, limited educational opportunities, and higher rates of violence in their communities.
The Administration for Children and Families states that poverty increases the likelihood of child abuse and neglect. Due to limited access to resources, children in poverty are at higher risk for malnutrition and developmental delays. Furthermore, impoverished parents may experience higher stress levels, which could contribute to more instances of violence and child abuse.
Schools in low-income communities often lack the resources necessary to provide adequate learning experiences for students. The U.S. Department of Education acknowledges that children from economically disadvantaged backgrounds are less likely to succeed academically than their more affluent peers. This disparity in educational opportunities has long-term consequences for these children’s futures.
Police and Child Safety
Police involvement plays a critical role in maintaining child safety. Law enforcement agencies collaborate with organizations such as the Administration for Children and Families to respond to incidences of child abuse and protect vulnerable children in high-risk environments.
Additionally, the Bezos Family Foundation works to create safe spaces for children and provide resources for at-risk families. By partnering with law enforcement and other community organizations, the foundation aims to reduce instances of violence, child abuse, and neglect.
